Biomass Briquettes and Pellets have become important players in the search for sustainable energy sources. These renewable energy sources provide advantages for the environment and the economy over conventional fossil fuels. This blog explores the complexities of biomass briquettes and pellets, including their environmental friendliness, the raw materials needed, the manufacturing process, marketing tactics, and profit margins.
Comprehending Biomass Briquettes and Pellets
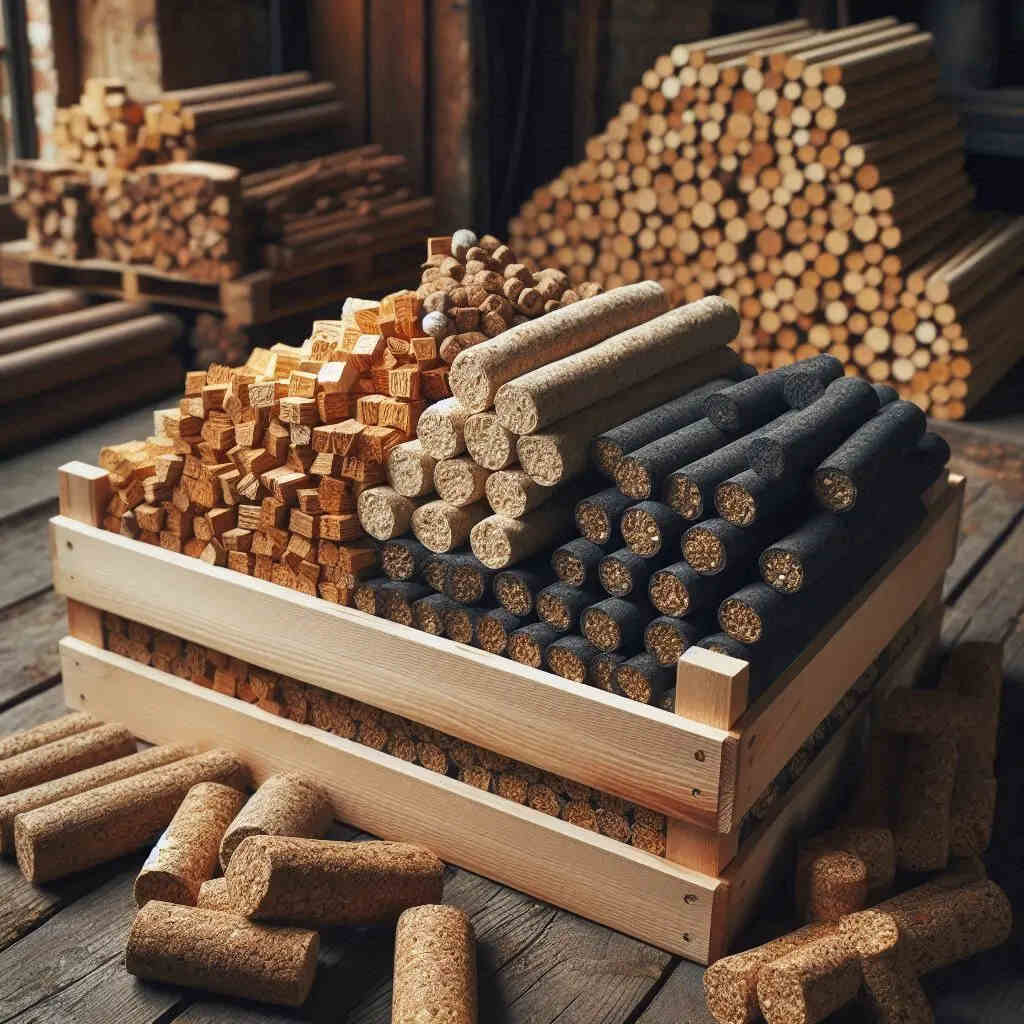

What are Biomass Briquettes and Pellets?
Compressed blocks or cylinders made of biomass resources are known as biomass briquettes and pellets. They serve as fuel for a number of purposes, such as industrial activities, cooking, and heating. Briquettes and pellets differ mostly in terms of size and shape. Pellets are small, cylindrical, and uniform in size, but briquettes are often larger and can be either rectangular or cylindrical.
Why opt for Biomass Briquettes and Pellets?
- Energy Source: Biomass is a renewable resource, in contrast to fossil fuels. Sustainable methods, like growing energy crops and using agricultural leftovers, can replenish it.
- Reduced Emissions: Compared to burning coal and other fossil fuels, burning biomass briquettes and pellets generates fewer emissions, which improves the quality of the air.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to fossil fuels, biomass is frequently less expensive, making it a financially feasible choice for energy generation.
- Waste Management: Producing biomass from forestry and agricultural residues lowers the danger of environmental pollution and aids in waste management.
Raw Materials for Biomass Briquettes and Pellets
Commonly Used Raw Materials
- Agricultural Waste: Straw, husks, and stalks are examples of crop waste that are frequently utilized. Rice husk, wheat straw, corn stover, and sugarcane bagasse are a few examples.
- Forestry Residues: From forestry activities, sawdust, wood chips, and bark are valuable raw resources.
- Energy Crops: Certain crops are grown expressly for biomass production, such as willow, miscanthus, and switchgrass.
- Industrial Waste: Sludge from paper mills and palm kernel shells are two examples of useful industrial byproducts.
Qualities of the Best Raw Materials
- Moisture level: To promote effective combustion and inhibit the growth of mold, the raw material should have a low moisture level, typically less than 15%.
- Elevated Calorific Value: When burned, materials possessing a higher calorific value release more energy.
- Low Ash Content: Combustion equipment needs less maintenance when using materials with low ash content because they leave fewer residues behind.
- Homogeneity: Uniform briquette and pellet quality is ensured by consistent particle size and content.
Manufacturing Process of Biomass Briquettes and Pellets
Detailed Manufacturing Procedure
- Gathering and Preparation of Raw Materials: After being gathered, the raw materials may need to be dried in order to lower their moisture content. You can use belt dryers, rotary dryers, or the sun to accomplish this.
- Grinding and Milling: Hammer mills or grinders are used to grind the dried materials into a fine powder. This guarantees consistent particle size for improved compaction.
- Mixing and Conditioning: To increase cohesiveness, the ground material is combined and frequently treated with a binding agent like molasses or starch.
- Pelletization/Briquetting: The processed material is fed into devices that either pelletize or briquet. These devices compress the material into pellets or briquettes using mechanical pressure.
- Cooling: To harden and stop the hot briquettes or pellets from collapsing, they are cooled using water or air cooling systems.
- Packaging and Storage: To preserve quality, the finished product is packed in bags or bulk containers and kept in a dry environment.
Types of Equipment Used
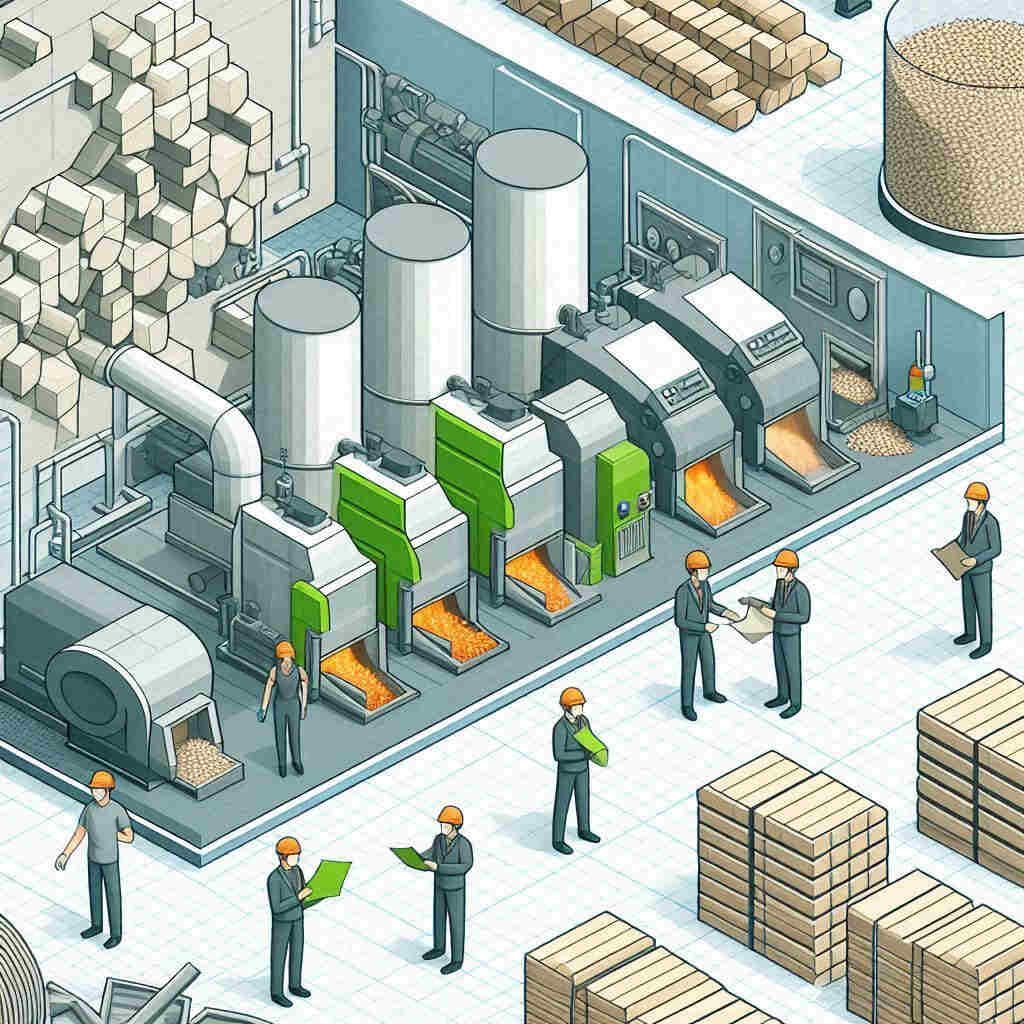
- Dryers: To lower the moisture content of unprocessed materials.
- Hammer mills and grinders are used to finely powder raw materials.
- Mixers: Used to combine binding agents with basic components.
- Equipment for briquette and pelletizing: Used to compress material into briquettes or pellets.
- Cooling Systems: To keep the finished product cold.
Marketing Strategies for Biomass Briquettes and Pellets
- Residential Sector: Homeowners who cook and heat their homes using biomass.
- The industrial sector is made up of businesses that use a lot of fuel for things like heating and steam production.
- The commercial sector includes establishments that use biomass for heating and cooking, like hotels and restaurants.
- Export markets: nations with substantial demand, particularly in Asia and Europe, for renewable energy sources.
Successful Marketing Techniques
- Emphasizing Environmental Benefits: In marketing campaigns, highlight how renewable and environmentally beneficial biomass briquettes and pellets are.
- Cost Comparisons: Highlight the financial benefits of switching to biomass instead of conventional fossil fuels.
- Quality assurance: To gain clients’ trust, maintain a high standard of quality and certification.
- Building Recognition for Your Brand: To promote the brand, use social media, trade exhibitions, and digital marketing.
- Forming Alliances: Work with companies and governmental organizations to advance the use of biomass as a sustainable energy.
Channels of Distribution
- Direct Sales: Selling products and services directly to customers and companies via physical stores and internet platforms.
- Distributors and Dealers: collaborating with distributors and dealers to reach a larger market.
- Bulk sales: Providing substantial volumes to businesses and industrial customers.
Profit Margins in Biomass Briquettes and Pellets Business
Elements That Affect Profit Margins
- Cost of Raw Materials: Profit margins can be greatly impacted by the price of raw materials. Using inexpensive, readily available resources locally can increase profitability.
- Production Efficiency: High-quality machinery and effective procedures lower production costs and boost margins.
- Market Demand: Better pricing and larger profit margins may result from strong demand and advantageous market conditions.
- Government Policies: Tax breaks, subsidies, and laws that support renewable energy can increase profits.
Calculating Profit Margins
- Revenue: Determine the total amount of money received from the sale of pellets and briquettes.
- Costs: These comprise the price of labor, raw materials, production, transportation, and marketing.
- Profit: To calculate the profit, deduct all costs from all revenue. A percentage of revenue can be used to express profit margins.
Case Study: Analysis of Profit Margin
Take into consideration the following fictitious numbers for a small-scale biomass briquette plant:
- Raw Material Cost: $30,000 per month
- Production Cost: $20,000 per month (including labor, energy, and maintenance)
- Marketing and Distribution Cost: $10,000 per month
- Total Monthly Cost: $60,000
- Monthly Production: 100 tons of briquettes
- Selling Price: $800 per ton
- Total Revenue: $80,000
- Monthly Profit: $80,000 (revenue) – $60,000 (cost) = $20,000
- Profit Margin: ($20,000 / $80,000) * 100 = 25%
A solid profit margin of 25% is shown in this case study, and it can be raised with effective cost control and manufacturing procedures.
Environmental Benefits of Biomass Briquettes and Pellets
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Carbon neutral biomass pellets and briquettes are produced. The carbon dioxide that the plants take during growth balances off the carbon dioxide that is emitted during combustion. When compared to fossil fuels, this balance aids in the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste Management
Waste management is aided by the creation of biomass from forestry and agricultural leftovers. It encourages environmentally friendly trash disposal methods and lowers the danger of environmental contamination.
Soil Fertility
The ash produced from burning biomass briquettes and pellets can be used as a soil amendment. It enriches the soil with essential nutrients, promoting healthy plant growth.
Energy Security
Because they offer a dependable and renewable energy source, biomass briquettes and pellets support energy security. They encourage the production of energy locally and lessen reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Air Quality Improvement
In comparison to burning coal and other fossil fuels, burning biomass briquettes and pellets results in lower pollution levels, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particle matter. As a result, there are fewer health hazards and better air quality.
Problems and Resolutions
Problems
- Availability and Cost of Raw resources: Seasonal changes and competition for raw resources might have an impact.
- Initial Investment: A substantial upfront investment in infrastructure and machinery is needed to set up a biomass briquette and pellet plant.
- Quality Control: Because raw materials differ, it might be difficult to maintain a constant level of quality.
- Market Acceptance: It can be challenging to persuade consumers to convert from conventional fuels to biomass.
Resolutions
- Diversifying Sources of Raw Materials: To guarantee a consistent supply of raw materials, combine forestry wastes, energy crops, and agricultural residues.
- Government Assistance: To lessen the initial investment burden, apply for grants, subsidies, and incentives from the government.
- Programs for Quality Assurance: To guarantee constant product quality, put in place stringent quality control procedures and certification schemes.
- Awareness Campaigns: Inform consumers about the advantages of biomass pellets and briquettes by holding awareness campaigns.
Conclusion
To address the world’s expanding energy needs, biomass briquettes and pellets provide a sustainable and environmentally beneficial option. Businesses can attain substantial profit margins and simultaneously contribute to environmental conservation by implementing efficient production processes, employing successful marketing tactics, and selecting the appropriate raw materials. In addition to being a business opportunity, the switch to biomass energy is an essential step towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. We can lessen our carbon footprint, efficiently manage waste, and guarantee future generations have access to safe and reliable electricity by embracing this renewable energy source.
What are Biomass Briquettes and Pellets?
Pellets and briquettes formed of compressed organic matter, or biomass, are renewable energy sources. These can consist of wood chips, sawdust, agricultural wastes, and other materials derived from plants.
Briquettes: Made by compressing biomass into a solid block, these are often larger in size and employed in industrial applications.
Pellets: Smaller and more homogeneous in size, these are typically cylindrical and employed in small-scale industrial applications or for home heating.
Because they employ waste materials and emit fewer greenhouse gases than fossil fuels, both types are regarded as environmentally benign substitutes.
What are the Benefits of Using Biomass Briquettes and Pellets?
The use of biomass pellets and briquettes has the following advantages:
1- Advantages for the Environment:
Carbon Neutral: Because the CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth balances the CO2 released after combustion, biomass is regarded as carbon neutral.
Waste reduction is the process of making use of forestry and agricultural waste that would otherwise be burned or allowed to decay.
2- Financial Gains:
Cost-effective: Frequently less expensive than fossil fuels, especially in areas with a surplus of biomass resources.
Employment Creation: In rural areas, local manufacturing of biomass pellets and briquettes might lead to job growth.
3- Energy Safety:
Renewable Resource: Biomass has the potential to lessen reliance on foreign fuel imports.
Consistent Supply: Compared to the erratic markets for fossil fuels, biomass supplies are typically more steady and predictable.
4- Effective and Pure Burning:
High Energy Density: When compared to raw biomass, briquettes and pellets have a higher energy density.
Lower Emissions: Compared to raw biomass or coal, they burn more cleanly and emit fewer particulates and other pollutants.


[…] your own food is one of the most essential components of Self Sustainable Lifestyle. To get you started, follow these […]